What is a VLAN A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) is a technology that allows you to separate a large network into smaller networks. Why would you want to do this? For security. For example, let’s say you have two departments, HR and IT. If you don’t want the HR department’s PCs to communicate with the IT department’s PCs, you would create two VLANs, one for each department. Then, you would create firewall rules to prevent the PCs from communicating with each other.
Setup VLAN
-
Log in to the Unifi portal. If it’s set to the default location, it will be at 192.168.1.1, or if you have remote management set up, go to the Unifi web portal and log in.
-
Go to Settings -> Networks.
-
Click “New Virtual Network.”
-
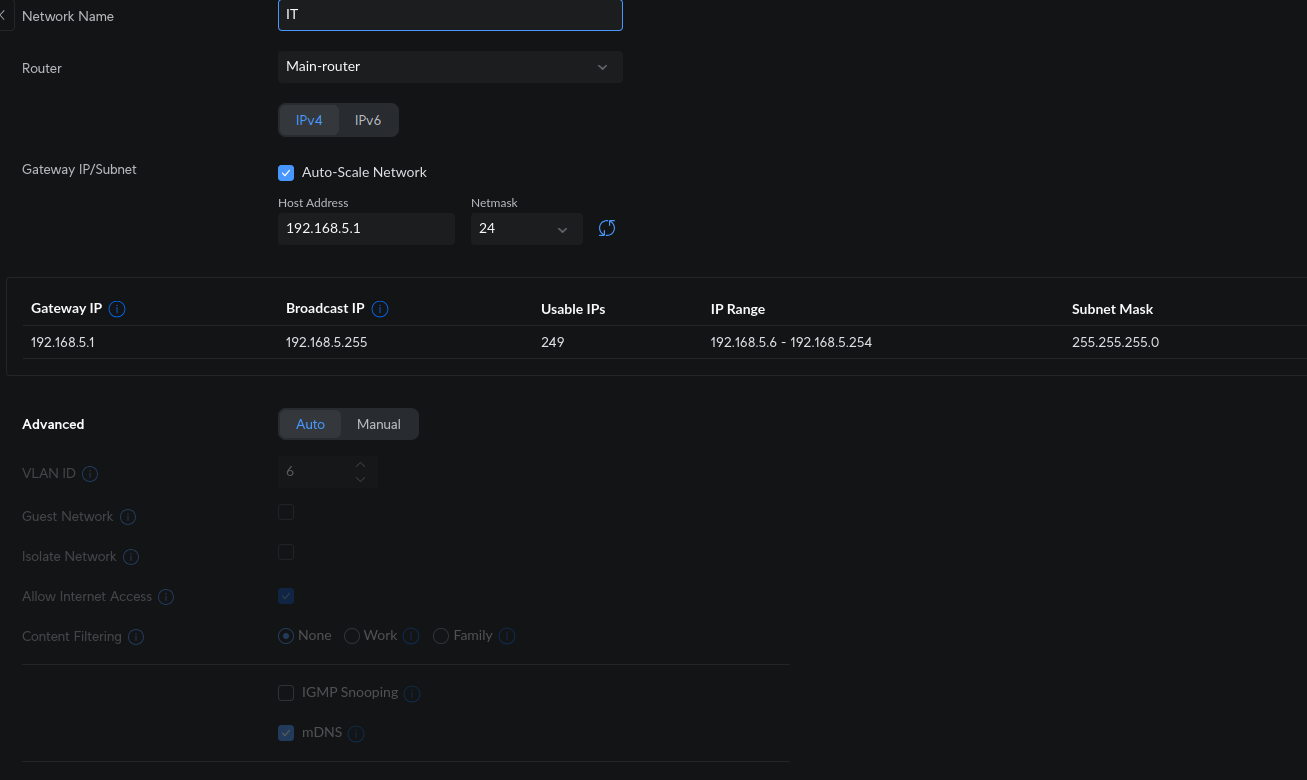
Give your VLAN a name.
-
For the gateway IP/subnet, you can set the host IP and netmask. The Auto-Scale Network option will automatically scale your network if you run out of IP addresses.
-
If you are happy with the settings, you can leave it at auto under advanced options, but here’s what each option does:
- VLAN ID: This is what each packet from that VLAN will be tagged with. If all of your networks have the same host bit, I would use the third octet as the ID number.
- Guest Network: Enabling this will set firewall rules so that the hosts can only access the internet or any PC on that network. If there is a guest portal, they will be redirected to it.
- Isolate Network: This option will only allow hosts to communicate with each other and no other VLAN.
- Allow Internet Access: This does exactly what it sounds like—hosts will have internet access.
- Content Filtering: This is simply a content filter.
-
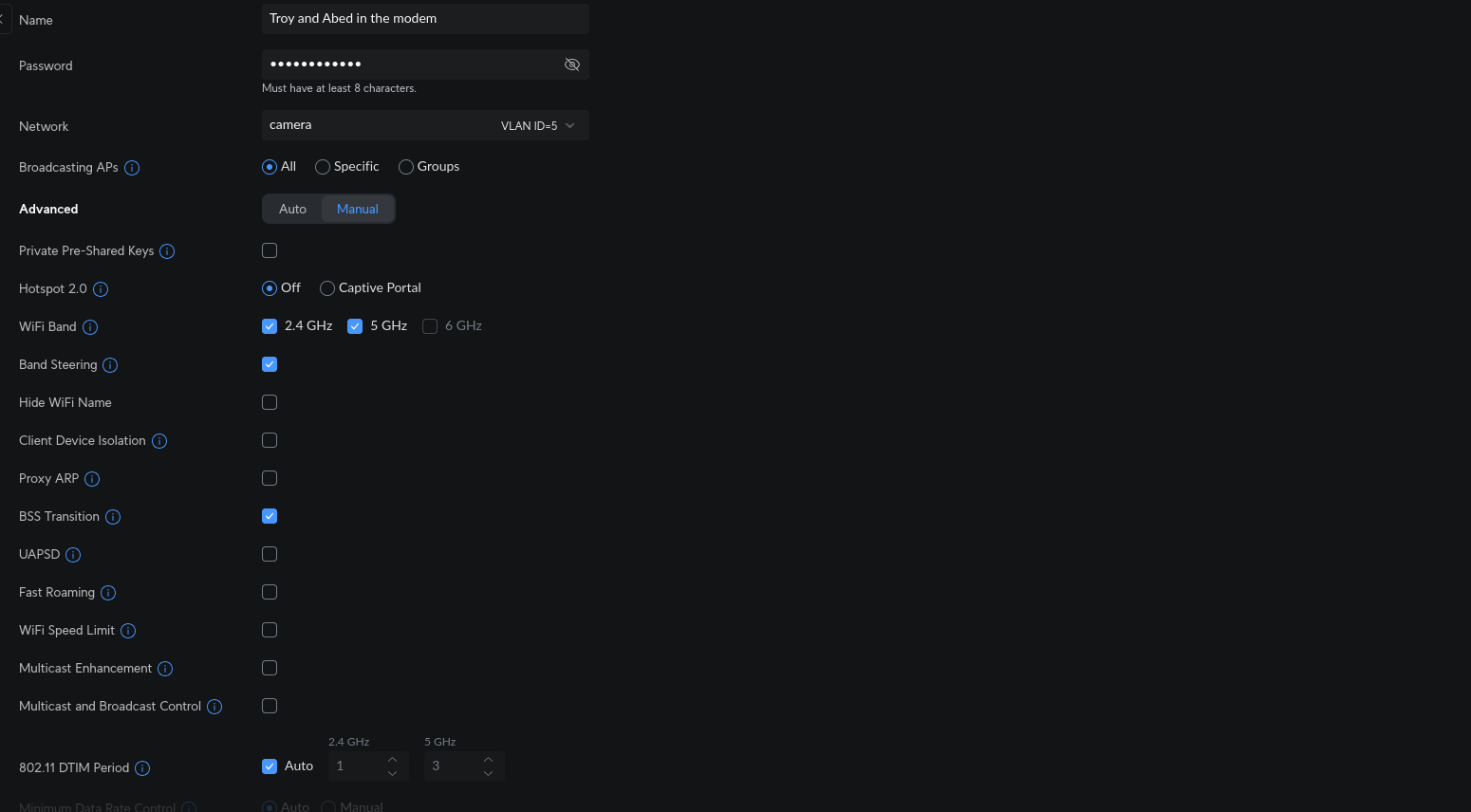
Then go to WiFi if you want WiFi for this VLAN. Just make sure you set the network setting to the VLAN you just created.
- Finally, go to Security -> Traffic & Firewall Rules to set up your firewall rules.